Contents
ToggleWhat Are The Biggest Cyber Threats in Smart Manufacturing?
The most significant cyber threats in smart manufacturing include targeted ransomware that halts production, operational technology hijacking that causes physical disruption, and data breaches that expose sensitive intellectual property, leading to substantial financial and reputational damage.
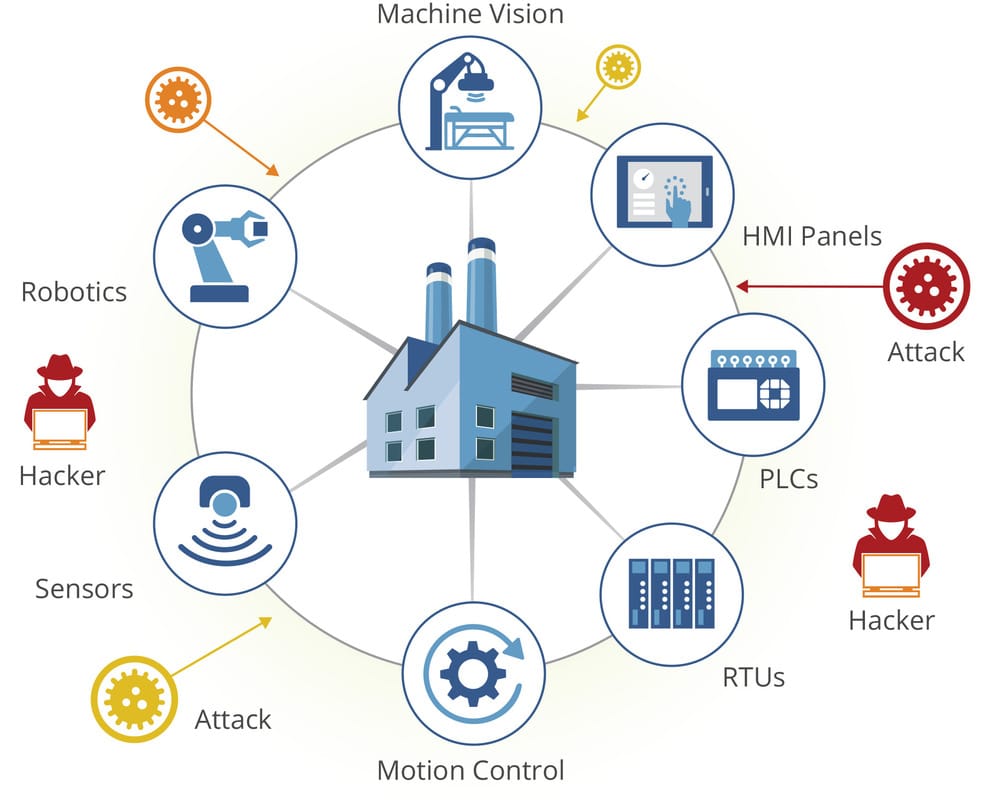
The convergence of Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) in Industry 4.0 has created an expanded attack surface for malicious actors. Previously air-gapped industrial networks are now connected to the internet, exposing them to a host of digital dangers.
According to a report by Gartner, by 2025, cyber-attackers will have weaponized industrial operational technology environments to successfully harm or kill humans. This highlights the critical need for robust security in the industrial iot in manufacturing sector. At Dev Station Technology, we see firsthand how these threats disrupt operations and innovate our protective strategies to counter them.
How Does Ransomware Affect Connected Factories?
Ransomware attacks on connected factories encrypt critical systems like Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs), causing immediate production stoppages, supply chain disruptions, and potential safety hazards until a ransom is paid or systems are restored.
Unlike in a typical IT environment, a ransomware attack in a factory does not just lock files; it stops physical processes. A 2023 report from Dragos, Inc. found that ransomware was the leading cause of industrial compromises. Imagine an automotive assembly line grinding to a halt because the robotic arms can no longer receive instructions. The financial impact is staggering. A factory producing goods worth $50,000 per hour could lose $1.2 million per day. Dev Station Technology helps implement backup and recovery solutions that isolate critical OT systems, allowing for rapid restoration of operations without paying a ransom.
What Is Operational Technology Hijacking?
Operational Technology (OT) hijacking is an attack where a malicious actor gains unauthorized control over industrial machinery, such as PLCs or SCADA systems, to manipulate physical processes. This can lead to equipment damage, production of faulty goods, or unsafe operating conditions.
The infamous Stuxnet worm, which targeted and destroyed centrifuges in an Iranian nuclear facility by manipulating their controllers, is a prime example of OT hijacking. In a modern factory, an attacker could alter the formula in a chemical mixing process, leading to a defective batch, or disable safety controls on heavy machinery, creating a dangerous environment for workers.
This type of attack is particularly insidious because it can go undetected for some time, with the damage being attributed to mechanical failure. Comprehensive 6 challenges of iot include securing these legacy OT devices, a specialty of our teams.

How Do Data Breaches Impact Production?
Data breaches in manufacturing can expose invaluable intellectual property, such as product designs, proprietary formulas, and production processes. The theft of this data can lead to loss of competitive advantage, counterfeit products, and significant long-term financial harm.
Beyond stealing IP, data breaches can also target operational data. For instance, an attacker could steal or alter quality control data to hide defects or steal production schedules to anticipate a company’s market moves. The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 revealed that the average cost of a data breach in the industrial sector was $4.47 million. This underscores the importance of a holistic security posture that protects both IT and OT data with equal rigor.
What Are the Main IoT Vulnerabilities in Factories?
The primary IoT vulnerabilities in factories stem from insecure device firmware with hardcoded credentials, unencrypted communication protocols that allow for data interception, and physically exposed or poorly configured endpoints that serve as easy entry points for attackers.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) devices are often designed for longevity and operational stability, not for security. Many are deployed with default passwords, outdated software, and limited capabilities for patching or updates. This creates a fertile ground for attackers to exploit. A 2022 survey by the SANS Institute found that a lack of visibility into device vulnerabilities was a top concern for OT security professionals.
Why Is Insecure Firmware a Major Risk?
Insecure firmware is a major risk because it can contain vulnerabilities like hardcoded passwords, unpatched security flaws, or lack secure boot mechanisms. Attackers can exploit these to gain complete control over a device, making it a permanent backdoor into the factory network.
Firmware is the software embedded in a hardware device. If an attacker can overwrite it with malicious code, the device is permanently compromised. The Mirai botnet, for example, spread by scanning for IoT devices with factory-default usernames and passwords. In a manufacturing setting, a compromised sensor could feed false data to control systems, or a compromised gateway could be used to launch attacks on other parts of the network. A critical best practice is secure secrets storage, ensuring no credentials are ever hardcoded in firmware.
How Can Communication Protocols Be Exploited?
Many legacy OT protocols like Modbus and modern IoT protocols like MQTT, if not configured securely, transmit data in plaintext. This allows attackers to perform man-in-the-middle attacks to eavesdrop on sensitive operational data or inject malicious commands.
An attacker on the same network could intercept a command sent to a PLC and change its parameters, such as increasing the pressure in a pipeline beyond safe limits. Without encryption, there is no way for the receiving device to verify the command’s authenticity. This is why Dev Station Technology emphasizes the use of secure protocol extensions like MQTT over TLS to encrypt data in transit and ensure data integrity.
What Security Frameworks Can Protect Smart Factories?
Effective security for smart factories is built upon modern frameworks like a Zero Trust architecture, which assumes no implicit trust; robust data encryption for data at rest and in transit; and network segmentation to contain breaches and limit an attacker’s lateral movement.
Protecting a smart factory requires moving beyond a traditional perimeter-based security model. It demands a defense-in-depth strategy that embeds security into every layer of the factory’s technology stack. This involves a cultural shift, often discussed in the context of devops vs devsecops, where security is a shared responsibility from the beginning of the system design lifecycle.
How Does a Zero Trust Architecture Work?
A zero trust architecture operates on the principle of never trust, always verify. Every user, device, and application must be authenticated and authorized before accessing any resource on the network, regardless of its location. This greatly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
In a Zero Trust model, a sensor requesting to send data to a cloud platform must first prove its identity, and the platform must verify it has permission to do so. This is a departure from older models where anything already inside the network was trusted. This principle of least privilege access ensures that even if one device is compromised, it cannot be used to easily access other systems. It is a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity strategy.
Why Is Data Encryption Non-Negotiable?
Data encryption is non-negotiable because it is the last line of defense. If an attacker bypasses other security measures and accesses data, encryption ensures that the data is unreadable and useless without the corresponding decryption key.
Understanding what is encryption is fundamental. It involves using algorithms to convert data into a secure format. In a smart factory, this applies to three states of data:
- Data in transit: Encrypting data as it moves between sensors, gateways, and the cloud using protocols like TLS.
- Data at rest: Encrypting data stored in databases or on servers in the cloud.
- Data in use: Utilizing confidential computing technologies to protect data while it is being processed.
How Does Network Segmentation Prevent Attacks?
Network segmentation divides a factory’s network into smaller, isolated zones. If an attacker compromises one zone, they are contained within it and cannot easily move laterally to attack critical systems in other zones. This is a core principle of robust network security.
For example, the network used for guest Wi-Fi should be completely separate from the OT network that controls the machinery. Similarly, the production line network in one part of the factory could be segmented from another. This is often achieved using firewalls and VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks). Proper segmentation can turn a potentially catastrophic, factory-wide shutdown into a minor, contained incident.
How Can AI Power Threat Detection in IIoT?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) can power threat detection by learning the normal behavior of an industrial network and automatically identifying anomalies or deviations that may indicate a cyberattack, providing a proactive defense mechanism.
Traditional security tools rely on known signatures of malware, which are ineffective against new, zero-day attacks. AI-based systems, however, do not need to know what an attack looks like. They only need to know what normal looks like. Any deviation from that baseline can trigger an alert for investigation.
What Is Anomaly Detection in Manufacturing?
Anomaly detection in manufacturing is the process of using machine learning models to analyze streams of data from sensors and network traffic to identify patterns that do not conform to expected behavior. This can detect both cyber threats and potential equipment malfunctions.
For example, an AI model could learn the normal vibration pattern of a motor. A sudden change in that pattern could indicate either a developing mechanical fault or that an attacker is trying to manipulate the motor’s speed. In another case, if a PLC that normally only communicates with its control server suddenly tries to connect to an unknown IP address on the internet, an anomaly detection system would immediately flag it as suspicious.
Which Compliance Standards Govern IIoT Security?
Key compliance standards that govern IIoT security include the NIST Cybersecurity Framework for overall risk management, ISO 27001 for information security management systems, and the ISA/IEC 62443 series, which is specifically designed for the security of industrial automation and control systems.
Adhering to these standards is not just about compliance; it is about implementing a proven, structured approach to cybersecurity. These frameworks provide a roadmap for companies to assess their security posture, identify gaps, and implement controls to mitigate risks. At Dev Station Technology, our solutions are designed to help clients meet and exceed the requirements of these critical standards.
What Does the NIST Cybersecurity Framework Advise?
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a high-level, strategic view of cybersecurity risk management organized around five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. It helps organizations structure their thinking and actions around managing cybersecurity risk.
This framework is technology-neutral and provides a common language for both technical and non-technical stakeholders to talk about cybersecurity. For a factory, this means:
- Identify: Know what assets you have on your network.
- Protect: Implement safeguards like access control and encryption.
- Detect: Continuously monitor for security events.
- Respond: Have a plan in place for when an incident occurs.
- Recover: Be able to restore operations quickly and safely.
How Do ISO 27001 and IEC 62443 Apply?
ISO 27001 is a broad standard for an Information Security Management System (ISMS), applicable to all organizations. IEC 62443 is a vertical standard specifically tailored for securing Industrial Automation and Control Systems (IACS), providing detailed technical requirements for OT environments.
While ISO 27001 provides the framework for managing information security as a whole, IEC 62443 gets into the specific technical details relevant to the factory floor. It defines security requirements for system integrators, product suppliers, and asset owners. Together, they provide a comprehensive approach to securing the entire smart manufacturing ecosystem, from corporate IT to the plant floor OT.
How Can Dev Station Technology Help Secure Your Factory?
Dev Station Technology provides a suite of services and solutions designed to address the unique cybersecurity challenges of smart manufacturing. We offer risk assessments, security architecture design, AI-powered monitoring, and implementation of robust IoT security controls to protect your operations from end to end.
Protecting a smart factory is a complex, continuous process, not a one-time fix. It requires deep expertise in both IT and OT security. Our team at Dev Station Technology has a proven track record of helping industrial clients navigate this complexity. We partner with you to develop and implement a security strategy that aligns with your operational goals and risk tolerance. We provide a holistic view of iot security to ensure every layer of your operation is protected.
To learn more about how we can help you build a resilient and secure smart manufacturing environment, we encourage you to explore our services at Dev Station Technology. Contact our team of experts for a consultation today by visiting our website at dev-station.tech or emailing us at sale@dev-station.tech.